Login to access
Want to subscribe?
This article is part of: Executive Briefing Service Executive Briefing Service
To find out more about how to join or access this report please contact us
In the next 10 years, many industries face the 'Great Compression' in which, in addition to the pressures of ongoing global economic uncertainty, there is also a major digital transformation that is destroying traditional value and moving it 'disruptively' to new areas and geographies. For the incumbent industry players we call the near-term results of this disruption 'The Digital Hunger Gap' – the widening deficit between past and projected revenues. This is our analysis of the top-level findings of the Silicon Valley Executive Brainstorm. (March 2013, Executive Briefing Service, Transformation Stream.) 10 Year Hunger Gap Mar 2013
Introduction
The Silicon Valley Brainstorm took place on 19-20 March 2013, at the Intercontinental Hotel, San Francisco.
Part of the New Digital Economics Executive Brainstorm & Innovation Series, it built on output from previous events in Singapore, Dubai, London and New York, and new market research and analysis, and focused on new business models and growth opportunities in digital commerce, content and the Internet of Things.
Summary Analysis: ‘The Great Compression’
In the next 10 years, many industries face the ‘Great Compression’ in which, in addition to the pressures of ongoing global economic uncertainty, there is also a major digital transformation that is destroying traditional value and moving it ‘disruptively’ to new areas and geographies, albeit at diminished levels.
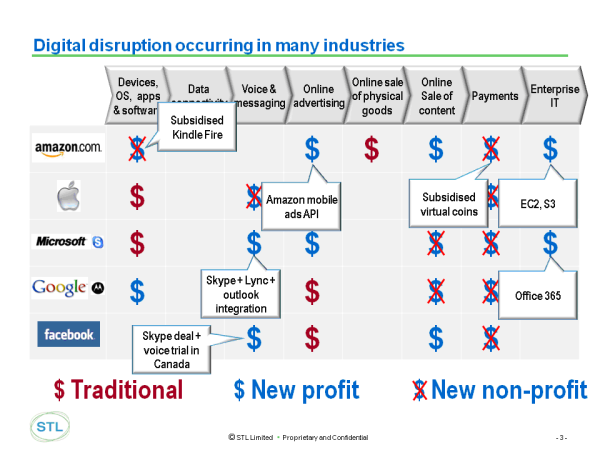
In previous analyses (e.g. Dealing with the ‘Disruptors’: Google, Apple, Facebook, Microsoft/Skype and Amazon) we have shown how key technology players in particular compete with different objectives in different parts of the digital value chain. Figure 1 below shows via crossed dollar signs (‘New Non-Profit’) the areas in which companies are competing without the primary intention of driving profits, which means that traditional competitors in those areas can expect ‘disruptive’ competition from new business models.
Figure 1 – Digital disruption
The Digital Hunger Gap
For the incumbent industry players we call the near-term results of this disruption ‘The Digital Hunger Gap’ – the widening deficit between past and projected revenues. Chris Barraclough, Chief Strategist STL Partners presented the classic Music Industry case study of the ‘Hunger Gap’ effects of digital disruption.
Figure 2 – The Music Industry’s ‘Hunger Gap’

In a vote, 95% of participants agreed that something similar would happen in other industries.
Chris then presented our initial analysis of the ‘Hunger Gap’ for telcos (to be published in full shortly), and asked the participants where they thought the telco industry would be relative to its 2012 position in 2020.
Figure 3 – Participants’ views on forecasts for the telecoms industry

As can be seen, participants’ views were widely spread, with a slight bias towards a more pessimistic outlook than that presented of a recovery to 2012 levels.
Chris argued that as the ‘hunger gap’ widens, and before new revenues are developed, there will be massive consolidation and cost-reduction among incumbent players, and opportunities for innovation in services, but the chances of success in the latter are very low and require a portfolio approach and either deep pockets, exceptional insight, or considerable good fortune.
Richard Kramer, Managing Partner of Arete Research, also presented a deflationary outlook for all but the leading consumer technology players in the handset and tablet arena.
Participants then voted on which areas needed the most significant changes in their business – and existing managements’ ‘mindset’ was voted as the top priority.
Figure 4 – ‘Mindset’ is the biggest barrier to transformation

It is also notable that all categories averaged 3.0 or over – or needing ‘Significant Change’. This points to a significant transformation across all industries.
Content:
- Opportunities
- Telco 2.0 Strategies
- Big Data and Personal Data
- Digital Commerce
- Digital Entertainment
- Mobile Advertising & Marketing
- The Internet of Things
- Outlook by Industry
- Next Steps
- Figure 1 – Digital disruption
- Figure 2 – The Music Industry’s ‘Hunger Gap’
- Figure 3 – Participants’ views on forecasts for the telecoms industry
- Figure 4 – ‘Mindset’ is the biggest barrier to transformation
- Figure 5 – The ‘Telco 2.0’ opportunities for CSPs
- Figure 6 – The impact of ‘Software Defined Networks’ (SDN)
- Figure 7 – Will ‘Personal Data’ be more useful than ‘Big Data’?
- Figure 8 – STL Partners’ ‘Wheel of Digital Commerce’
- Figure 9 – Who will in ‘SoMoLo’?
- Figure 10 – Significant changes in viewing habits
- Figure 11 – Transformation needed in the advertising industry
- Figure 12 – Growth projections for M2M ‘mobile’ (e.g. 3G/4G) connected devices
