The Great Compression: surviving the ‘Digital Hunger Gap’
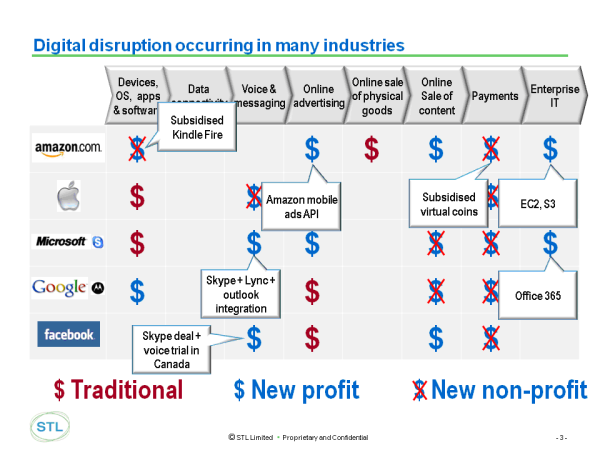
In the next 10 years, many industries face the ‘Great Compression’ in which, in addition to the pressures of ongoing global economic uncertainty, there is also a major digital transformation that is destroying traditional value and moving it ‘disruptively’ to new areas and geographies. For the incumbent industry players we call the near-term results of this disruption ‘The Digital Hunger Gap’ – the widening deficit between past and projected revenues. This is our analysis of the top-level findings of the Silicon Valley Executive Brainstorm. (March 2013, Executive Briefing Service, Transformation Stream.)
10 Year Hunger Gap Mar 2013

