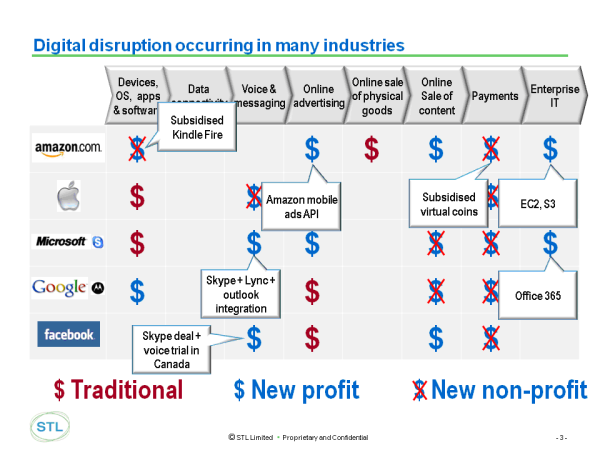
Telco Opportunities in the ‘New Mobile Web’?
The transformed mobile web experience, brought about by the adoption of a range of new technologies, is creating a new arena for operators seeking to (re)build their role in the digital marketplace. Operators are potentially well-placed to succeed in this space; they have the requisite assets and capabilities and the desire to grow their digital businesses. This report examines the findings of interviews and a survey conducted amongst key industry players, supplemented by STL Partners’ research and analysis, with the objective of determining the opportunities for operators in the New Mobile Web and the strategies they can implement in order to succeed. (September 2013, Foundation 2.0, Executive Briefing Service.)
Operator Opportunities in the “New Mobile Web”