Login to access
Want to subscribe?
This article is part of: Executive Briefing Service Executive Briefing Service
To find out more about how to join or access this report please contact us
As connectivity has become commoditised, launching new network technology can no longer be relied upon to generate operator growth. This report outlines eight guiding principles for operators seeking to move beyond connectivity into tailored vertical solutions.
===============================================================
The chartpack for this report is available to download as an additional file
STL Partners has long believed that telecoms operators need to and can do more to add value to their consumer and enterprise customers and to society more generally. For the telecoms industry, the need to do more is illustrated by flat or declining revenues and rising capital expenditure and debt levels. The opportunity for telecoms to add more value is also clear. The demands of society now call for greater coordination between all players and new technology – 5G, analytics, AI, automation, cloud – is now spawning the Coordination Age.
Figure 1: The Coordination Age – new paradigm, new telco purpose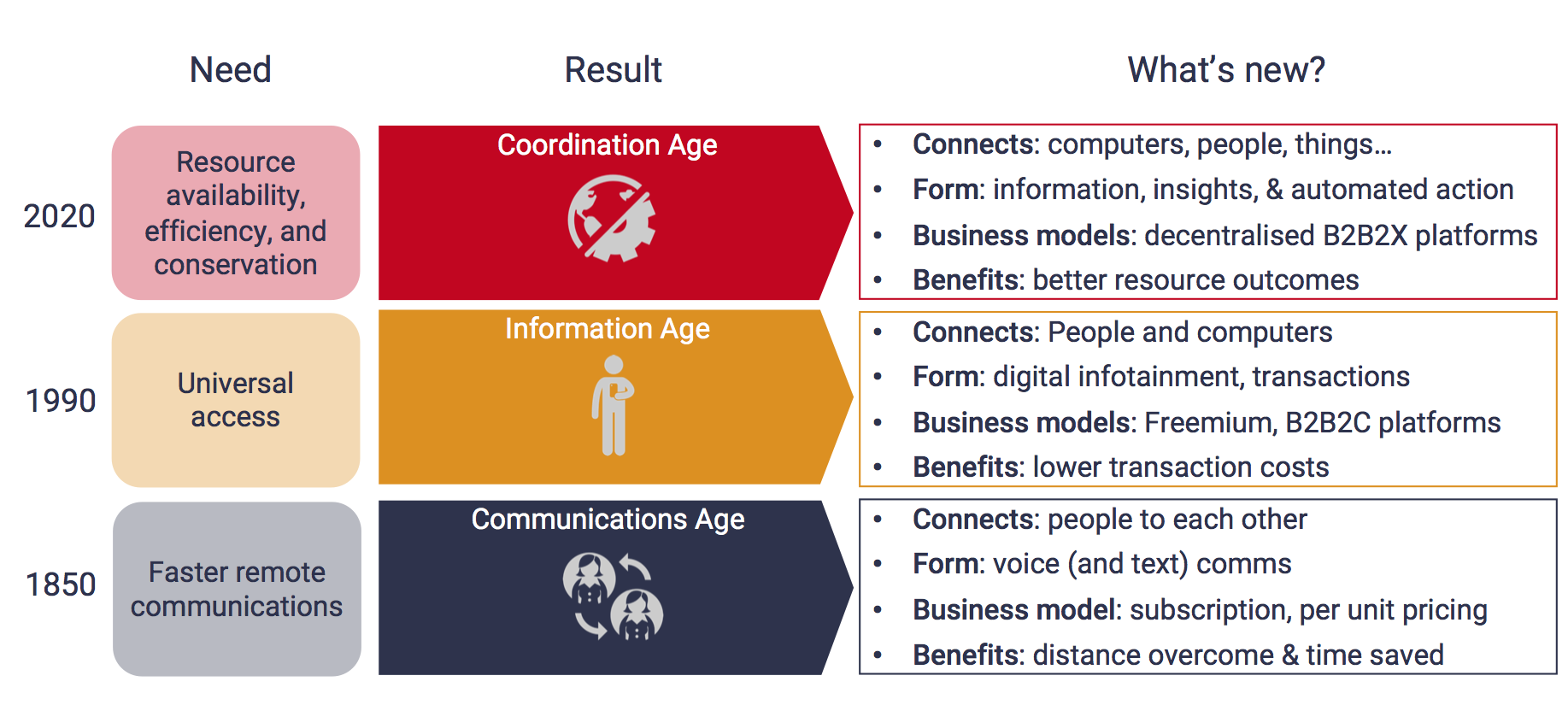
Source: STL Partners
Operators have the credibility, skills and relationships to contribute more in the Coordination Age. But the opportunity will not drop into their laps. Improved networks are not, of themselves, the driver of new value: it accrues to the provider of services that run on the network and it is up to operators to develop platforms and services that exploit ubiquitous, high-bandwidth connectivity.
So far, operators have found moving beyond connectivity challenging. There are a handful of success stories; most attempts to develop vertical solutions have failed to move the needle. In this report, we draw on successes and failures from within and outside telecoms to outline 8 core guiding principles for ambitious leaders within the telecoms industry who are determined to help their organisations to deliver more than connectivity.
Enter your details below to request an extract of the report
5G: A catalyst for change
In some ways, the challenge/opportunity for mobile operators has been present for the last 5-10 years: limited incremental revenue growth in voice, messaging, and data.
However, 5G is a catalyst for real change. There are internal pressures from the investments being made that mean operators must create new revenue streams. More positive reasons relate to increased demand for telco-driven services and the technological changes that telcos have implemented which will help the commercial side to adapt. Below are some of the main reasons why 5G has created a resurgent need to change business models.
- Making returns on network investments: It’s a given that 5G cannot be delivered without significant investment by the operators: be it in spectrum acquisition, upgrading the RAN and core network, managing a more distributed architecture of small cells, etc. Telcos can focus on ensuring that network runs efficiently to maintain margins, however many will need to look to new services. Data usage will surge, but the price customers will pay for each gigabyte will decline at a disproportionate rate.
- Building on telco cloud and edge computing platforms: Telcos have started to invest in developing their networks to become more like the cloud platforms that underpin the large cloud providers’ services. In fact, it’s a key part of the 5G core. Part of this has been the move towards SDN, network virtualisation and integrating edge computing. This flexible platform will allow telcos to innovate quickly and create new differentiated services on top if they have the desire to change their financial and operational models.
- Unlocking an enterprise business: Before 5G, mobile operators’ enterprise businesses have involved selling SIMs to enterprise customers with some forays into value-added services, such as cloud storage, mobile device management and M2M communications. Enterprises are genuinely interested in 5G and the capabilities it brings. For some, 5G has become an umbrella term for technological innovation. This is a good thing for the mobile industry, as it means enterprises will open doors to telcos and be keen to engage them for new solutions.
- Creating business value: 5G’s unique capabilities will enable use cases that solve real problems, particularly in industrial transformation. This last point is exemplified by research STL Partners previously conducted on the business value 5G brings to certain verticals by enhancing productivity, increasing output, creating efficiencies, etc. However, much of this value is extracted by the applications, solutions and services on top of the underlying network.
Figure 2: 5G enabled use cases could increase GDP by $1.5 trillion by 2030

Source: STL Partners
Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- 5G: A catalyst for chang
- Guiding principles for mobile operators seeking to move beyond connectivity
- Select priority verticals and how you will compete in the them
- Adopt a new approach to resource allocation: less CapEx and more OpEx
- Material OpEx should focus on building new skills, assets, capabilities, relationships
- Establish senior management commitment and independence for the new venture
- Focus on commercial as well as technological differentiation in order to disrupt verticals
- De-emphasise network integration – at least to start with
- Recognise that M&A will be needed for market entry in most cases
- Realise that organic growth can work in exceptional operator or market circumstances
- Conclusion
