Login to access
Want to subscribe?
This article is part of: Executive Briefing Service
To find out more about how to join or access this report please contact us
T-Mobile USA’s ‘uncarrier’ strategy has delivered significant net additions, but is it a good strategy - and is the disruption promised by Softbank CEO Masayoshi Son already underway? We compare it to Free Mobile’s disruptive approach in France, and the results of its competitors’ responses.
Introduction
Ever since the original Softbank bid for Sprint-Nextel, the industry has been awaiting a wave of price disruption in the United States, the world’s biggest and richest mobile market, and one which is still very much dominated by the dynamic duo, Verizon Wireless and AT&T Mobility.
Figure 1: The US, a rich and high-spending market
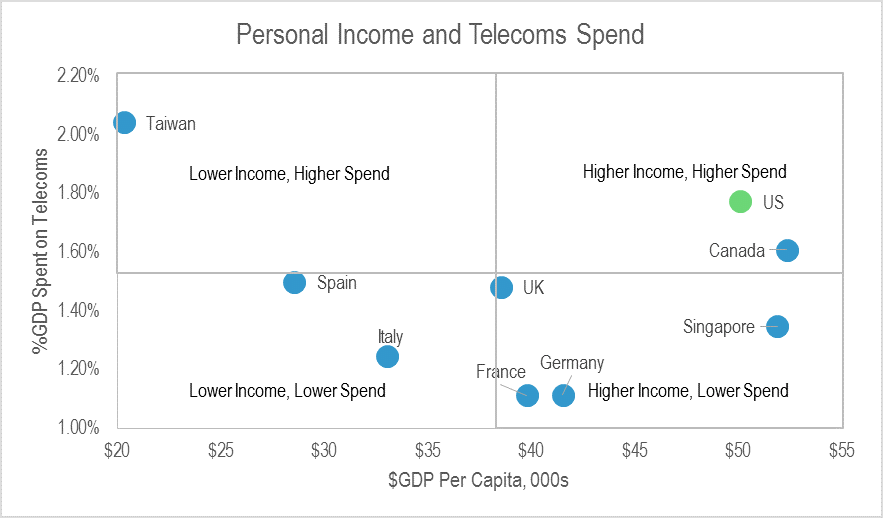
Source: Onavo, Ofcom, CMT, BNETZA, TIA, KCC, Telco accounts, STL Partners
However, the Sprint-Softbank deal saga delayed any aggressive move by Sprint for some time, and in the meantime T-Mobile USA stole a march, implemented its own very similar ‘uncarrier’ proposition strategy, and achieved a dramatic turnaround of their customer numbers.
As Figure 2 shows, the duopoly marches on, with Verizon in the lead, although the gap with AT&T has closed a little lately. Sprint, meanwhile, looks moribund, while T-Mobile has closed half the gap with the duopolists in an astonishingly short period of time.
Figure 2: The duopolists hold a lead, but a new challenger arises…

Now, a Sprint-T-Mobile merger is seriously on the cards. Again, Softbank CEO Masayoshi Son is on record as promising to launch a price war. But to what extent is a Free Mobile-like disruption event already happening? And what strategies are carriers adopting?
For more STL analysis of the US cellular market, read the original Sprint-Softbank EB , the Telco 2.0 Transformation Index sections on Verizon and AT&T , and our Self-Disruption: How Sprint Blew It EB . Additional coverage of the fixed domain can be found in the Triple-Play in the USA: Infrastructure Pays Off EB and the Telco 2.0 Index sections mentioned above
The US Market is Changing
In our previous analysis Self-Disruption: How Sprint Blew It, we used the following chart, Figure 3, under the title “…And ARPU is Holding Up”. Updating it with the latest data, it becomes clear that ARPU – and in this case pricing – is no longer holding up so well. Rather than across-the-board deflation, though, we are instead seeing increasingly diverse strategies.
Figure 3: US carriers are pursuing diverse pricing strategies, faced with change
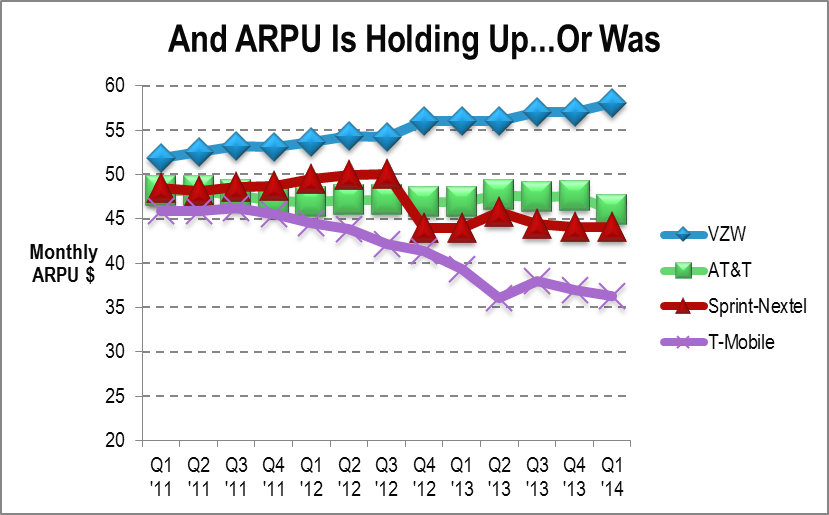
Source: STL Partners
AT&T’s ARPU is being very gradually eroded (it’s come down by $5 since Q1 2011), while Sprint’s plunged sharply with the shutdown of Nextel (see report referenced above for more detail). Since then, AT&T and Sprint have been close to parity, a situation AT&T management surely can’t be satisfied with. T-Mobile USA has slashed prices so much that the “uncarrier” has given up $10 of monthly ARPU since the beginning of 2012. And Verizon Wireless has added almost as much monthly ARPU in the same timeframe.
Each carrier has adopted a different approach in this period:
- T-Mobile has gone hell-for-leather after net adds at any price.
- AT&T has tried to compete with T-Mobile’s price slashing by offering more hardware and bigger bundles and matching T-Mobile’s eye-catching initiatives, while trying to hold the line on headline pricing, perhaps hoping to limit the damage and wait for Deutsche Telekom to tire of the spending. For example, AT&T recently increased its device activation fee by $4, citing the increased number of smartphone activations under its early-upgrade plan. This does not appear in service-ARPU or in headline pricing, but it most certainly does contribute to revenue, and even more so, to margin.
- Verizon Wireless has declined to get involved in the price war, and has concentrated on maintaining its status as a premium brand, selling on coverage, speed, and capacity. As the above chart shows, this effort to achieve network differentiation has met with a considerable degree of success.
- Sprint, meanwhile, is responding tactically with initiatives like its “Framily” tariff, while sorting out the network, but is mostly just suffering. The sharp drop in mid-2012 is a signature of high-value SMB customers fleeing the shutdown of Nextel, as discussed in Self-Disruption: How Sprint Blew It.
Figure 4: Something went wrong at Sprint in mid-2012

Source: STL Partners, Sprint filings
- Executive Summary
- Contents
- Introduction
- The US Market is Changing
- Where are the Customers Coming From?
- Free Mobile: A Warning from History?
- T-Mobile, the Expensive Disruptor
- Handset subsidy: it’s not going anywhere
- Summarising change in the US and French cellular markets
- Conclusions
- Figure 1: The US, a rich and high-spending market
- Figure 2: The duopolists hold a lead, but a new challenger arises…
- Figure 3: US carriers are pursuing diverse pricing strategies, faced with change
- Figure 4: Something went wrong at Sprint in mid-2012
- Figure 5: US subscriber net-adds by source
- Figure 6: The impact of disruption – prices fall across the board
- Figure 7: Free’s spectacular growth in subscribers – but who was losing out?
- Figure 8: The main force of Free Mobile’s disruption didn’t fall on the carriers
- Figure 9: Disruption in France primarily manifested itself in subscriber growth, falling ARPU, and the death of the MVNOs
- Figure 10: T-Mobile has so far extended $3bn of credit to its smartphone customers
- Figure 11: T-Mobile’s losses on device sales are large and increasing, driven by smartphone volumes
- Figure 12: Size and profitability still go together in US mobile – although this conceals a lot of change below the surface
- Figure 13: Fully-developed disruption, in France
- Figure 14: Quality beats quantity. Sprint repeatedly outspent VZW on its network
