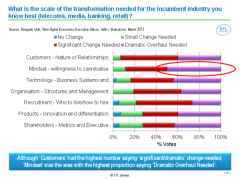
Value is squeezed out of industries as they become increasingly digital – i.e. accessed by mobile and online, driven by data and defined by software. We call the collective economic impact of this pressure ‘The Great Compression’. But which companies will survive and prosper – and how? 90% of the Execs at our Silicon Valley brainstorm identified ‘management mindset’ as a key factor in Telecoms, Media, Finance and Retail. Our analysis and a detailed report of the findings of the Digital Economy session at the NDE Executive Brainstorm, Silicon Valley, held at the InterContinental Hotel, San Francisco on the 19th March 2013. (May 2013, Executive Briefing Service, Transformation Stream).
Scale of Transformation Needed April 2013