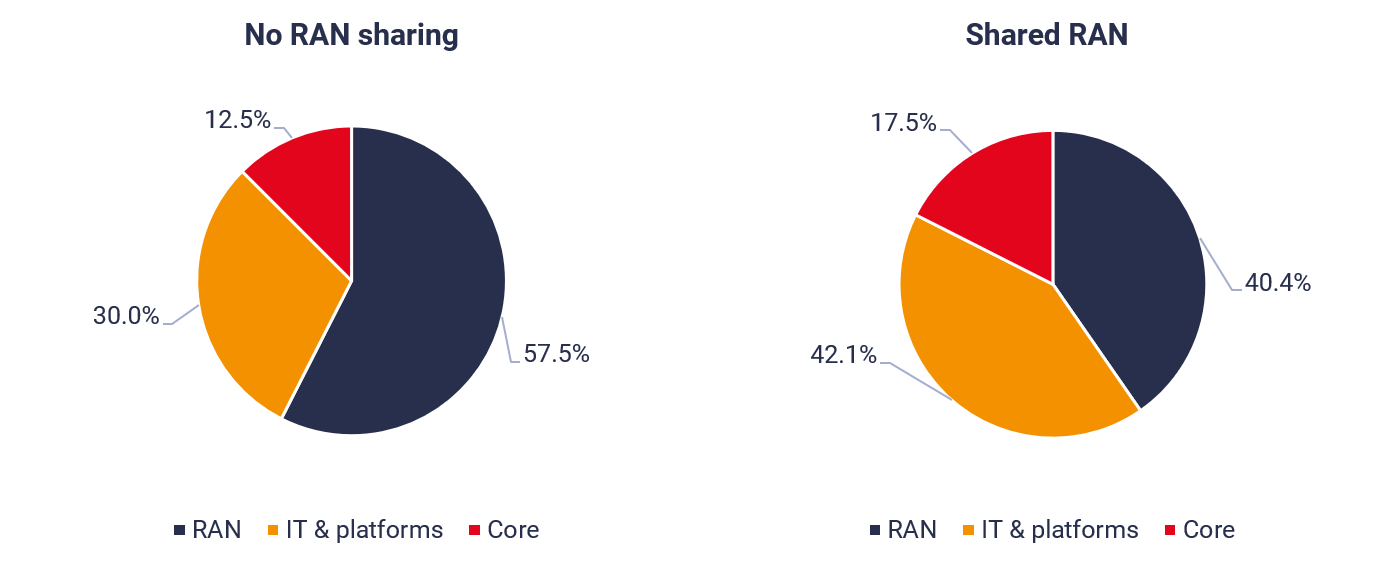
The largest part of the costs of building and operating a mobile network are in the radio access network (RAN). In 5G, where higher frequencies, especially in the mmWave bands, have limited reach, the cost implications of deploying more base stations will be significant. For example, based on our research into the cost breakdown across networks and IT for the average mobile network operator, the addition of 50% more base stations could increase the proportion of network costs absorbed by the RAN from a typical 57.5% to 67%. This includes elements such as acquiring land rights and leasing costs.
Passive sharing of sites alone will provide useful savings, but to minimise these costs MNOs will need to consider active sharing of base stations and other elements of the RAN as a means of reducing costs. For example, on a multi-operator RAN, each operator has its own spectrum, but they share the radio equipment, antennae and often the backhaul. Some costs such as management overhead cannot meaningfully be shared, but such an arrangement could enable operators to reduce total RAN operating costs by up to 45%. This will apply particularly in crowded areas, where sites will be scarce so operators will increasingly have to engage in active network sharing to be able to accommodate the RAN equipment.